Diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa refers to a medical finding characterized by a widespread, slightly reddish appearance of the mucous membranes, which are the moist tissues that line the body's internal cavities and passages.
This condition can be caused by various factors, including inflammation, infection, or irritation. It is commonly observed in certain medical conditions, such as esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus), gastritis (inflammation of the stomach), or inflammatory bowel disease (a group of conditions that cause inflammation of the digestive tract).
Diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa is often a sign of underlying health issues and may require further evaluation and treatment to address the underlying cause.
In summary, diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa is a medical finding that indicates a widespread, slightly reddish appearance of the mucous membranes. It is commonly associated with inflammation, infection, or irritation and can be a sign of underlying health issues.
Diffuse Mildly Erythematous Mucosa
Diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa is a medical finding that indicates a widespread, slightly reddish appearance of the mucous membranes, which are the moist tissues that line the body's internal cavities and passages. It can be caused by various factors, including inflammation, infection, or irritation, and is commonly associated with certain medical conditions such as esophagitis, gastritis, or inflammatory bowel disease.
- Diffuse: Widespread, involving a large area
- Mildly: Slightly, not severe
- Erythematous: Reddish in color
- Mucosa: Mucous membranes
- Inflammation: A response to injury or infection, characterized by redness, swelling, heat, and pain
- Infection: Caused by the presence of harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria or viruses
- Irritation: A state of discomfort or annoyance caused by contact with a substance or object
- Esophagitis: Inflammation of the esophagus
- Gastritis: Inflammation of the stomach
- Inflammatory bowel disease: A group of conditions that cause inflammation of the digestive tract
These key aspects highlight the various dimensions of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, including its widespread nature, mild severity, reddish appearance, and association with inflammation, infection, irritation, and certain medical conditions. Understanding these aspects is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of this condition.
Diffuse
In the context of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, the term "diffuse" signifies that the erythema, or redness, is spread over a large area of the mucous membranes. This widespread involvement is a key characteristic of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, distinguishing it from localized areas of erythema.
The diffuse nature of erythema in diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa can provide valuable insights for diagnosis and management. For instance, in esophagitis, diffuse erythema may indicate a more severe or extensive inflammatory process compared to localized erythema. Similarly, in inflammatory bowel disease, diffuse erythema may suggest a more widespread involvement of the digestive tract.
Understanding the diffuse nature of erythema in diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa is crucial for appropriate evaluation and treatment. It allows healthcare professionals to assess the extent and severity of the underlying condition and determine the most suitable course of action.
Mildly
In the context of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, the term "mildly" signifies that the erythema, or redness, is not severe. This subtle presentation is a key characteristic of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, distinguishing it from more severe forms of mucosal inflammation.
The mild severity of erythema in diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa can be attributed to various factors, including the underlying cause, duration, and individual patient response. For instance, in esophagitis, mildly erythematous mucosa may indicate an early stage of inflammation or a milder form of the condition. Similarly, in inflammatory bowel disease, mildly erythematous mucosa may suggest a less active or localized inflammatory process.
- Facet 1: Early Detection and Intervention
The mildly erythematous nature of the mucosa can facilitate early detection and intervention, allowing for prompt treatment and potentially preventing progression to more severe stages.
- Facet 2: Prognosis and Management
The mild severity of erythema can influence prognosis and management decisions. Patients with mildly erythematous mucosa may have a more favorable prognosis and require less aggressive treatment compared to those with severe erythema.
- Facet 3: Differential Diagnosis
Mildly erythematous mucosa can help differentiate between various conditions. For instance, in the differential diagnosis of esophagitis, mildly erythematous mucosa may suggest a non-erosive form of the condition, as opposed to more severe forms with erosions or ulcerations.
- Facet 4: Monitoring Disease Activity
Monitoring changes in the severity of erythema can provide insights into disease activity and response to treatment. In inflammatory bowel disease, for example, a reduction in erythema may indicate a positive response to therapy and disease remission.
Understanding the mild severity of erythema in diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa is crucial for appropriate evaluation and management. It allows healthcare professionals to assess the extent and activity of the underlying condition and determine the most suitable course of action, including the need for further diagnostic tests, treatment options, and monitoring strategies.
Erythematous
Erythema, the medical term for redness of the skin or mucous membranes, is a key characteristic of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa. It results from vasodilation, or the widening of blood vessels, which increases blood flow to the affected area. This increased blood flow causes the area to appear red and inflamed.
In the context of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, the erythema is typically mild and widespread, covering a large surface area of the mucous membranes. This can be caused by various factors, including inflammation, infection, or irritation. For instance, in esophagitis, erythema of the esophageal mucosa may be due to inflammation caused by acid reflux or other irritants.
Recognizing the erythematous component of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management. By identifying the underlying cause of the erythema, healthcare professionals can determine the most suitable course of action, which may include medications to reduce inflammation, antibiotics to treat infection, or lifestyle modifications to address irritants.
Overall, the erythematous nature of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa is a significant indicator of underlying health issues and plays a vital role in guiding diagnosis and treatment decisions.
Mucosa
Mucous membranes, also known as mucosa, are moist tissues that line the body's internal cavities and passages, such as the digestive tract, respiratory tract, and urogenital tract. They play a crucial role in protecting the body from external threats, such as pathogens and toxins, while also facilitating various physiological functions.
- Facet 1: Protective Barrier
Mucous membranes form a protective barrier against harmful substances, preventing their entry into the body. They secrete mucus, a thick fluid that traps and removes foreign particles, pathogens, and irritants.
- Facet 2: Absorption and Secretion
Mucous membranes are involved in the absorption of nutrients and water, as well as the secretion of various substances, such as enzymes, hormones, and antibodies.
- Facet 3: Lubrication and Protection
The mucus produced by mucous membranes lubricates and protects the underlying tissues, reducing friction and preventing damage.
- Facet 4: Immune Function
Mucous membranes are part of the immune system, containing specialized cells that can recognize and respond to pathogens, triggering immune responses to protect the body.
In the context of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, understanding the role of mucous membranes is crucial. Erythema, or redness, of the mucous membranes can indicate inflammation, infection, or irritation. By examining the characteristics of the erythema, such as its location, extent, and severity, healthcare professionals can gain insights into the underlying cause and determine the appropriate course of action.
Inflammation
Inflammation is a complex biological process that plays a crucial role in the body's response to injury or infection. It involves the activation of various immune cells and chemical mediators, leading to a cascade of events characterized by redness, swelling, heat, and pain.
- Facet 1: Protective Response
Inflammation serves as a protective response to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. It helps to isolate and eliminate the offending agents, promoting healing and repair.
- Facet 2: Tissue Damage
While inflammation is essential for defense and healing, excessive or chronic inflammation can lead to tissue damage and contribute to the development of various diseases.
- Facet 3: Clinical Signs
The classic signs of inflammationredness, swelling, heat, and painare caused by increased blood flow, fluid accumulation, and the release of inflammatory mediators.
- Facet 4: Systemic Effects
In severe cases, inflammation can trigger systemic effects, such as fever, chills, and fatigue, as part of the body's overall response to injury or infection.
In the context of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, inflammation plays a significant role in the development of this condition. Erythema, or redness, is a key indicator of inflammation in the mucous membranes, which are moist tissues lining the body's internal cavities and passages. Understanding the connection between inflammation and diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Infection
Infection plays a significant role in the development of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa. When harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria or viruses, invade and multiply within the body, they trigger an inflammatory response, leading to redness and other symptoms associated with diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa.
Bacteria and viruses can enter the body through various routes, such as the respiratory tract, digestive tract, or through breaks in the skin. Once inside the body, they can attach to and invade the mucous membranes, causing inflammation and damage. The immune system responds to the infection by sending white blood cells and other immune cells to the site of infection, leading to the characteristic signs of inflammation: redness, swelling, heat, and pain.
In the context of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, infection can be caused by a variety of microorganisms, including:
- Bacteria, such as Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and Helicobacter pylori
- Viruses, such as herpes simplex virus, Epstein-Barr virus, and cytomegalovirus
- Fungi, such as Candida and Aspergillus
- Parasites, such as Giardia and Entamoeba histolytica
Understanding the connection between infection and diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. By identifying the underlying infectious agent, healthcare professionals can determine the most effective course of action, which may include antibiotics, antiviral medications, or other therapies to eliminate the infection and resolve the inflammation.
In summary, infection is a major contributing factor to the development of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa. Recognizing the role of infection in this condition is essential for effective diagnosis and management, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Irritation
Irritation is a common cause of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, a condition characterized by widespread mild redness of the mucous membranes. When an irritant comes into contact with the mucous membranes, it triggers an inflammatory response, leading to erythema and other symptoms.
- Facet 1: Common Irritants
Various substances and objects can act as irritants, including chemicals, allergens, and physical agents. Common examples include harsh detergents, fragrances, tobacco smoke, and excessive heat.
- Facet 2: Mechanisms of Irritation
Irritants can damage the protective layer of the mucous membranes, allowing harmful substances to penetrate and trigger an inflammatory response. They can also directly activate inflammatory cells, leading to the release of mediators that cause redness and swelling.
- Facet 3: Impact on Diffuse Mildly Erythematous Mucosa
In the context of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, irritation can be a primary cause or an exacerbating factor. For instance, in patients with esophagitis, exposure to gastric acid and bile can irritate the esophageal mucosa, leading to inflammation and erythema.
- Facet 4: Management and Prevention
Managing irritation involves identifying and avoiding triggers. In cases of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, healthcare professionals may recommend lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes or avoiding certain substances, to reduce irritation and promote healing.
Understanding the connection between irritation and diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa is essential for effective diagnosis and management. By recognizing the role of irritants, healthcare professionals can provide targeted advice and interventions to alleviate symptoms and prevent further damage to the mucous membranes.
Esophagitis
Esophagitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the esophagus, the muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. This inflammation can be caused by various factors, including acid reflux, infections, and certain medications. Esophagitis is a common component of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, a condition characterized by widespread mild redness of the mucous membranes.
In the context of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, esophagitis contributes to the erythema, or redness, of the esophageal mucosa. The inflammatory process in esophagitis leads to increased blood flow and dilation of blood vessels in the esophageal mucosa, resulting in the characteristic reddish appearance. Additionally, esophagitis can cause erosion and ulceration of the esophageal mucosa, further contributing to the erythema and other symptoms.
Recognizing the connection between esophagitis and diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management. By identifying esophagitis as an underlying cause, healthcare professionals can determine the most effective course of treatment, which may include medications to reduce inflammation, proton pump inhibitors to suppress acid production, or lifestyle modifications to avoid triggers.
In summary, esophagitis is a significant component of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, contributing to the erythema and other symptoms. Understanding this connection is essential for effective diagnosis and management, ultimately improving patient outcomes and preventing complications.
Gastritis
Gastritis, an inflammation of the stomach's lining, plays a significant role in the development and characteristics of "diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa," a condition marked by widespread mild redness of the mucous membranes. Understanding this connection is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
- Facet 1: Underlying Cause of Erythema
Gastritis causes inflammation of the gastric mucosa, leading to increased blood flow and dilation of blood vessels. This results in the characteristic erythema, or redness, observed in diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa.
- Facet 2: Contributing to Mucosal Damage
Gastritis can cause erosion and ulceration of the gastric mucosa, further contributing to the erythema and other symptoms of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa. The damaged mucosa becomes more susceptible to irritation and inflammation, perpetuating the cycle.
- Facet 3: Differential Diagnosis
Recognizing the connection between gastritis and diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa is crucial for differential diagnosis. By identifying gastritis as an underlying cause, healthcare professionals can distinguish it from other conditions with similar symptoms, such as esophagitis or inflammatory bowel disease.
- Facet 4: Guiding Treatment Approach
Understanding the role of gastritis in diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa helps guide the treatment approach. Medications to reduce inflammation, such as proton pump inhibitors or H2 blockers, are often prescribed to address gastritis and alleviate the associated symptoms of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa.
In summary, gastritis is a key component of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, contributing to its characteristic erythema and other symptoms. Recognizing this connection is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management, ultimately improving patient outcomes and preventing complications.
Inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) encompasses a range of conditions that cause chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. It plays a significant role in the development and characteristics of "diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa," a condition characterized by widespread mild redness of the mucous membranes. Understanding this connection is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
- Facet 1: Underlying Pathophysiology
IBD leads to inflammation and damage of the digestive tract mucosa, including the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. This inflammation causes increased blood flow and dilation of blood vessels in the affected mucosa, resulting in the characteristic erythema, or redness, observed in diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa.
- Facet 2: Contributing to Mucosal Damage
IBD can cause erosion and ulceration of the digestive tract mucosa, further contributing to the erythema and other symptoms of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa. The damaged mucosa becomes more susceptible to irritation and inflammation, perpetuating the cycle.
- Facet 3: Differential Diagnosis
Recognizing the connection between IBD and diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa is crucial for differential diagnosis. By identifying IBD as an underlying cause, healthcare professionals can distinguish it from other conditions with similar symptoms, such as esophagitis or gastritis.
- Facet 4: Guiding Treatment Approach
Understanding the role of IBD in diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa helps guide the treatment approach. Medications to reduce inflammation, such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressive drugs, are often prescribed to address IBD and alleviate the associated symptoms of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa.
In summary, IBD is a key component of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, contributing to its characteristic erythema and other symptoms. Recognizing this connection is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management, ultimately improving patient outcomes and preventing complications.
Frequently Asked Questions about Diffuse Mildly Erythematous Mucosa
This section aims to address common concerns and misconceptions surrounding diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, providing concise and informative answers.
Question 1: What is diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa?
Diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa refers to a medical finding characterized by a widespread, slightly reddish appearance of the mucous membranes, which line the body's internal cavities and passages.
Question 2: What causes diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa?
Diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa can be caused by various factors, including inflammation, infection, or irritation. Common underlying conditions associated with this finding include esophagitis, gastritis, and inflammatory bowel disease.
Question 3: Is diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa a serious condition?
While diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa itself is not typically a serious condition, it often indicates underlying health issues that may require further evaluation and treatment. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience this finding to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate care.
Question 4: How is diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa diagnosed?
Diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa is diagnosed through a physical examination, typically performed by a healthcare professional using specialized instruments to visualize the affected areas.
Question 5: How is diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa treated?
The treatment for diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa depends on the underlying cause. Treatment may involve medications to reduce inflammation, antibiotics to treat infection, or lifestyle modifications to address irritants.
Question 6: Can diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa be prevented?
While not always preventable, certain measures can help reduce the risk of developing diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa. These include avoiding known irritants, maintaining a healthy diet, and managing underlying medical conditions that may contribute to inflammation.
Understanding diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa and its potential causes is crucial for appropriate evaluation and management. If you experience this finding, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and receive proper care.
Transition to the next article section: Understanding the causes and significance of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa is essential for effective patient care. The following section will delve into the clinical implications and management strategies for this condition.
Tips for Managing Diffuse Mildly Erythematous Mucosa
Diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, characterized by widespread mild redness of the mucous membranes, can indicate underlying health issues that require proper management. Here are some essential tips to consider:
Tip 1: Seek Medical Evaluation
If you experience diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. A healthcare professional can determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment.
Tip 2: Address Underlying Conditions
Managing the underlying medical condition causing diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa is essential. This may involve medications, lifestyle modifications, or other therapies as recommended by your healthcare provider.
Tip 3: Avoid Irritants
Identifying and avoiding potential irritants that may exacerbate diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa is important. Common irritants include spicy foods, acidic beverages, and certain medications.
Tip 4: Maintain Oral Hygiene
Practicing good oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing, can help prevent infection and irritation of the oral mucosa, which may contribute to diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa.
Tip 5: Quit Smoking
Smoking can irritate and damage the mucous membranes, worsening diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa. Quitting smoking is highly recommended to improve overall health and reduce mucosal inflammation.
Tip 6: Manage Stress
Chronic stress can contribute to inflammation throughout the body, including the mucous membranes. Incorporating stress-reducing techniques, such as exercise, meditation, or yoga, can be beneficial.
Tip 7: Follow a Healthy Diet
Maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support overall well-being and reduce inflammation, which may benefit diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa.
Tip 8: Stay Hydrated
Adequate hydration is essential for maintaining healthy mucous membranes. Drinking plenty of fluids, such as water or herbal teas, can help soothe and protect the mucosa.
Following these tips can help manage diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, promote overall health, and prevent complications. Remember to consult with your healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment recommendations.
Conclusion
Diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa, a condition characterized by widespread, slightly reddened mucous membranes, can indicate underlying health concerns that warrant attention. Prompt medical evaluation is crucial to determine the cause and initiate appropriate treatment.
Understanding the causes and significance of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa is essential for effective patient care. Healthcare providers play a vital role in diagnosing and managing this condition, guiding patients towards optimal outcomes and preventing complications.
Further research and advancements in medical understanding can contribute to a deeper comprehension of diffuse mildly erythematous mucosa and its implications for overall health. By staying informed and working in collaboration with healthcare professionals, individuals can effectively manage this condition and maintain their well-being.
Uncover The Truth: Felix Jose's Salary Revealed
Unlocking The Secrets Of Carla Diab's Parents: Unveiling The Roots Of Success
Brenda Benet's Son Revealed: Uncovering The Hidden Truth
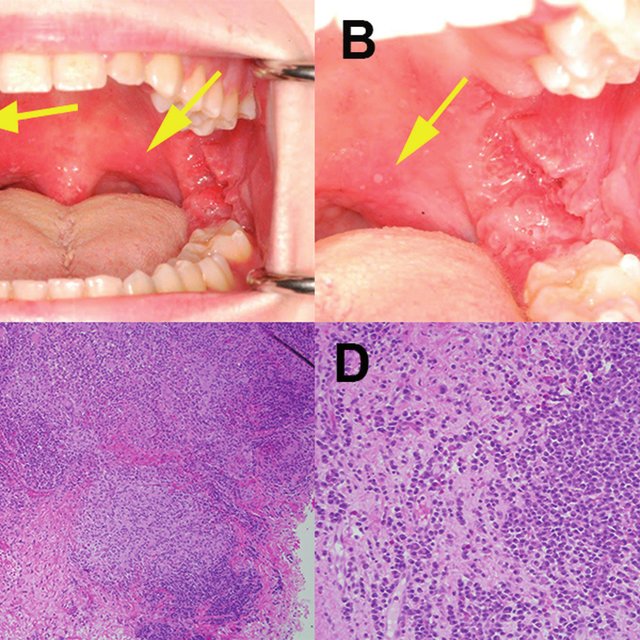
(A,B) Areas of mildly erythematous mucosa and multiple aphthous ulcers
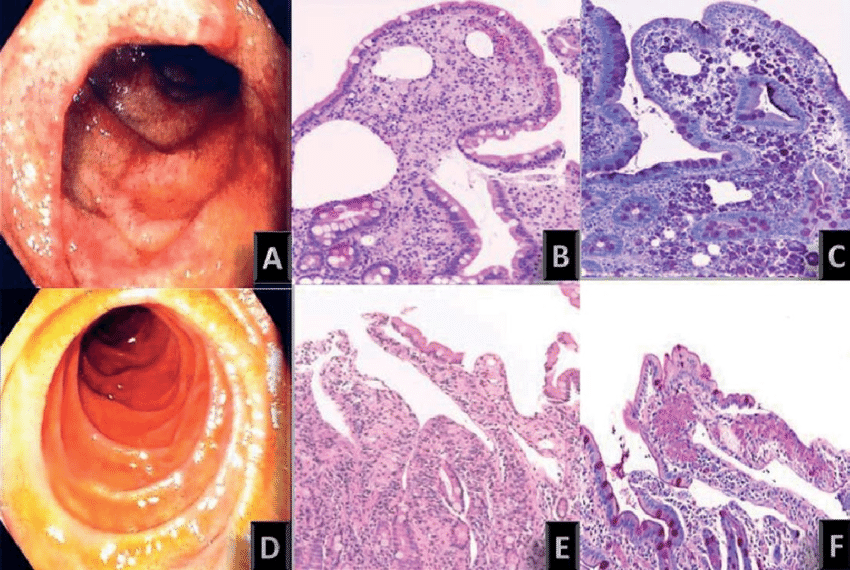
Erythematosus duodenal mucosa with diffuse haemorrhagic suffusions (A
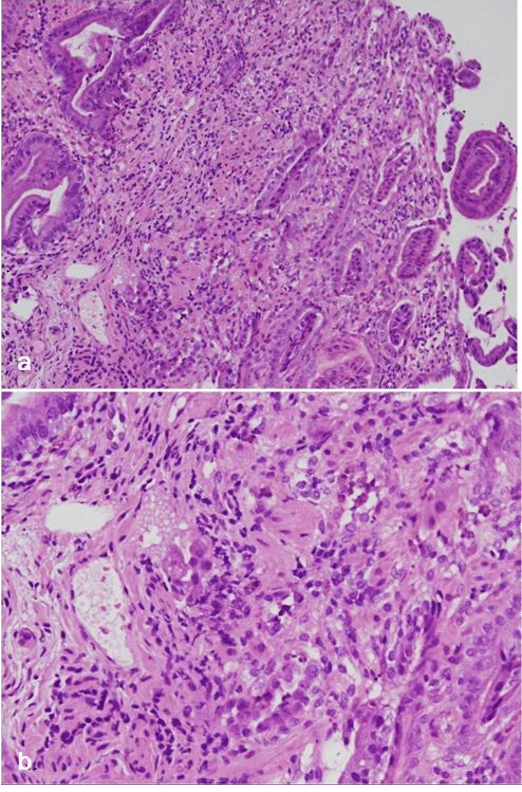
Endoscopic findings showing a. Gastric antrum Erythematous mucosa
ncG1vNJzZmifp6h%2Bb63MrGpnnJmctrWty6ianpmeqL2ir8SsZZynnWSxqrLFrqqeZZ2euaW42Gacq7GknbKurdOorKxlnaqwsL%2FAZ5%2BtpZw%3D